Neurology & Neurosurgery
Neurology & Neurosurgery
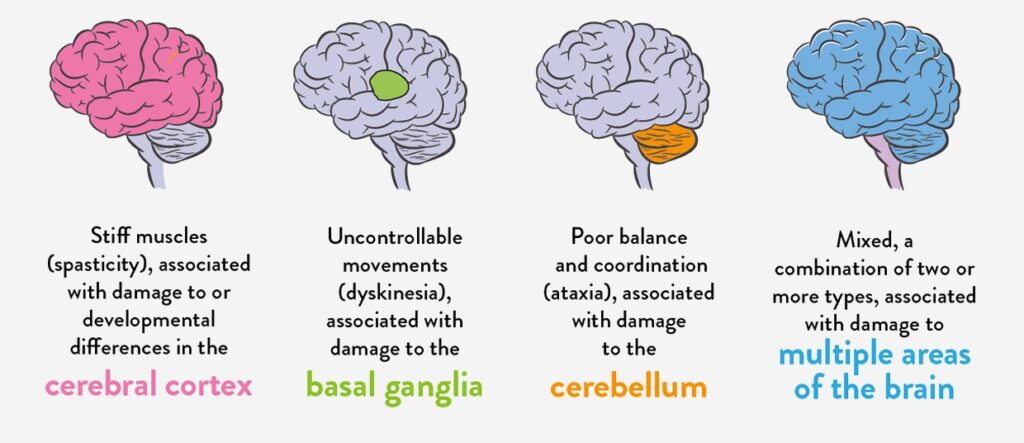
Cerebral Palsy
Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome
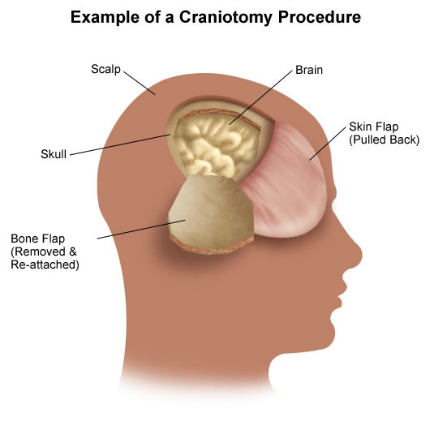
Craniotomy (Excision of brain tumor)
A craniotomy is the surgical removal of part of the bone from the skull to expose the brain. Specialized tools are used to remove the section of bone called the bone flap. The bone flap is temporarily removed, then replaced after the brain surgery has been done.
Some craniotomy procedures may use the guidance of computers and imaging (magnetic resonance imaging [MRI] or computerized tomography [CT] scans) to reach the precise location within the brain that is to be treated. This technique requires the use of a frame placed onto the skull or a frameless system using superficially placed markers or landmarks on the scalp. When either of these imaging procedures is used along with the craniotomy procedure, it is called stereotactic craniotomy.
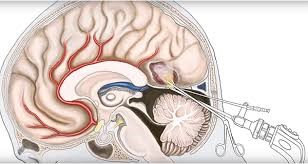
Burr Holes
Burr holes are small holes that a neurosurgeon makes in the skull. Burr holes are used to help relieve pressure on the brain when fluid, such as blood, builds up and starts to compress brain tissue.
A layer of thin tissues called meninges surround and help protect the brain. These meninges contain blood vessels that carry blood to and from the brain. The dura is the outermost of these meninges. A head injury can cause one or more of these blood vessels to tear and bleed. A sudden tear might cause blood to build up very suddenly. With a small tear, the blood might build up more slowly. Blood might start to build up just below the dura mater. This causes something called a subdural hematoma. Tears in different blood vessels may cause blood to build up just above the dura layer, causing an epidural hematoma. A hematoma is when blood collects in an area and causes swelling.
This buildup of blood is dangerous. As the blood builds, it pushes up against the skull and has nowhere to go. If the blood starts to compress the brain, it can lead to symptoms or even death if not treated.
Deep Breath Stimulation Brain Surgery
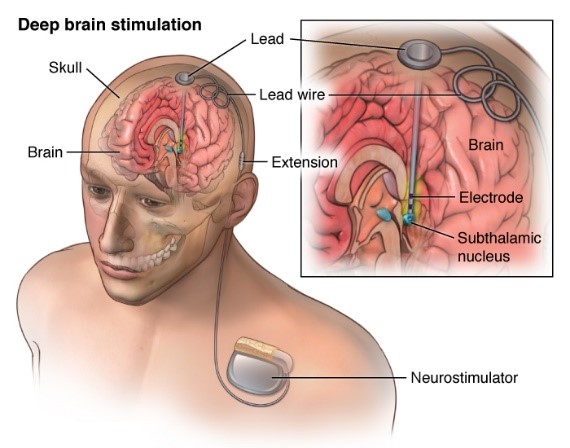
Dystonia
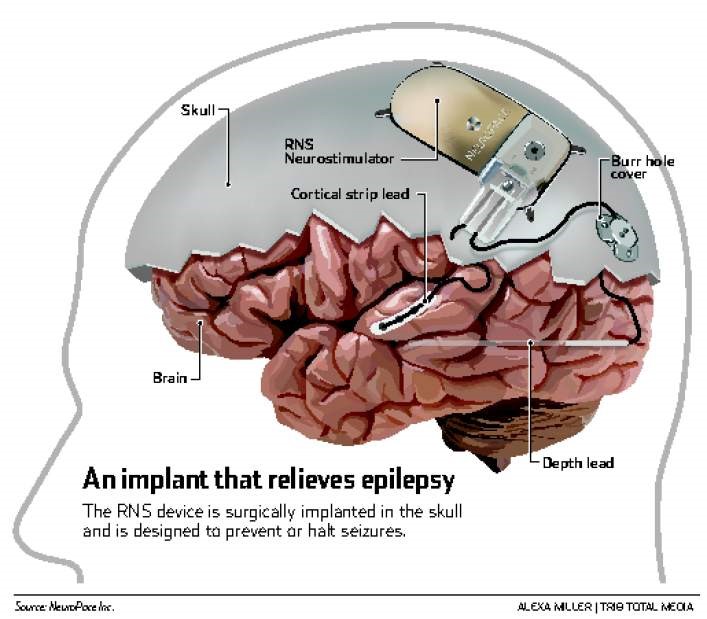
Epilepsy Surgery
Multiple sclerosis
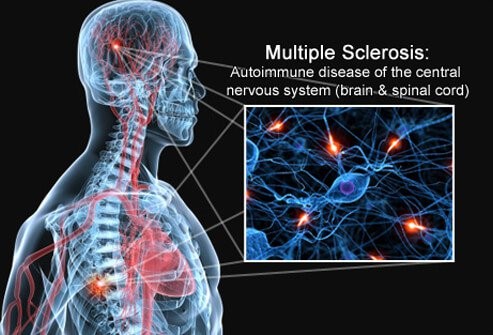
- Within the CNS, the immune system attacks myelin – the fatty substance that surrounds and insulates the nerve fibres -as well as the nerve fibres themselves.
- The damaged myelin forms scar tissue (sclerosis), which gives the disease its name.
- When any part of the myelin sheath or nerve fibre is damaged or destroyed, nerve impulses traveling to and from the brain and spinal cord are distorted or interrupted, producing a wide variety of symptoms.
- The disease is thought to be triggered in a genetically susceptible individual by a combination of one or more environmental factors.
- People with MS typically experience one of four disease courses, which can be mild, moderate or severe.
Neurosurgical Oncology
Parkinson's Disease
- Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects predominately dopamine-producing (“dopaminergic”) neurons in a specific area of the brain called substantia nigra.
- Symptoms generally develop slowly over years. The progression of symptoms is often a bit different from one person to another due to the diversity of the disease. People with PD may experience:
- Tremor, mainly at rest and described as pill rolling tremor in hands. Other forms of tremor are possible
- Slowness of movements (bradykinesia)
- Limb rigidity
- Gait and balance problems
Stroke
Vascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery

Numerous thrombogenic devices are available that can be delivered through microcatheters to permanently occlude cerebral vascular abnormalities. Catheter technology perfected in the coronary circulation for the management of atherosclerotic disease has been used to treat similar lesions of the extracranial and intracranial cerebral circulation.
Cerebral circulation angioplasty for vasospasm has become an accepted technique, and superselective drug delivery is growing in popularity. This chapter reviews the recent literature in vascular and endovascular neurosurgery in an attempt to familiarize the reader with recent advances in the management of cerebrovascular disease.

Aarav Medicare team is ready to look after all your medical emergency needs. We will Take care of your health.
Saurav
Why Aarav Medicare?

Highly Qualified Specialists
Best Specialist Doctors for all the Treatment and Procedures. Get Free Online Consutations.
State Of The Art Facility
Finest Hospitals with all the modern Medical Equipment and Best Patient Care.
