ENT
ENT
Acoustic Neuroma (Schwannoma)
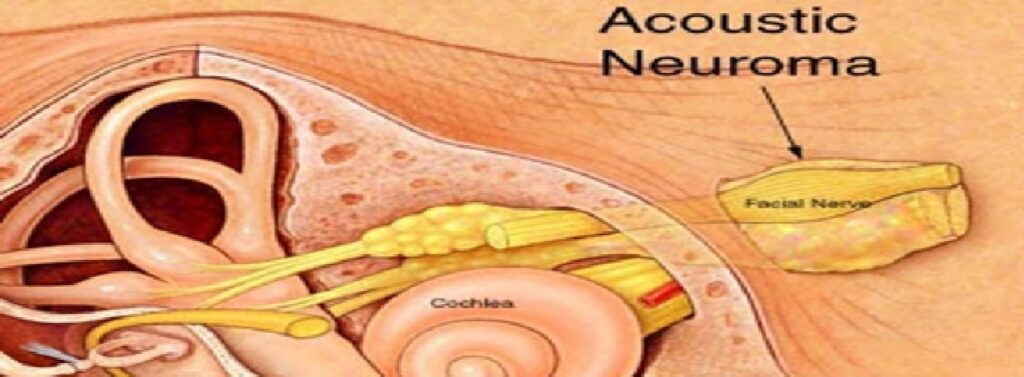
An acoustic neuroma is a benign tumor that has the potential to affect a patient’s balance and hearing nerves. Acoustic neuroma tumors most often occur on one side of the patient’s brain, tend to be slow growing and do not metastasize to other portions of the body.
The most common symptoms include decreased hearing and ringing sound in the ear called tinnitus. Other symptoms may include loss of balance, facial numbness or tingling, and in rare cases of very large tumors, confusion and headaches.
Treatment options depend upon the patient age and tumor size. Some tumors can be observed over a span of time to determine the tumor growth pattern. Hearing preservation surgery can lead to favorable long-term outcomes in patients with smaller tumors. Large tumors that compress the brainstem are often surgically removed. Preserving the facial nerve function is a top priority during surgical removal of acoustic neuromas with postoperative function being very favorable when the tumor is small.
Hearing Restoration Surgery/Stapedectomy
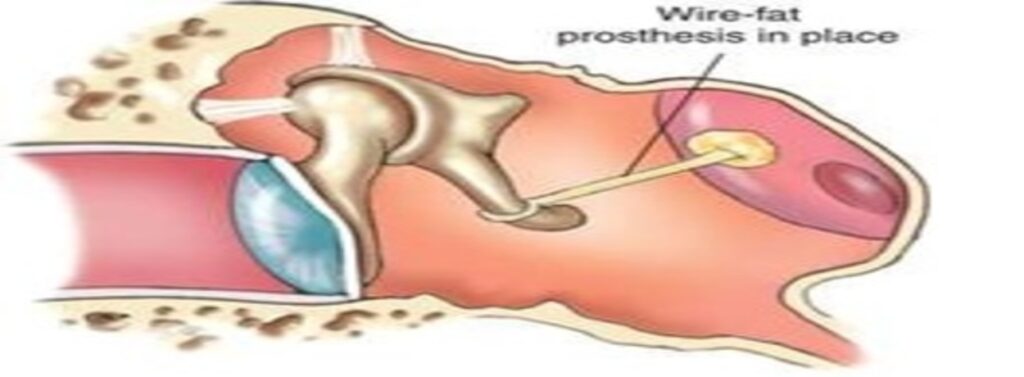
A stapedectomy is ear surgery that can be done to treat hearing loss caused by a problem called otosclerosis. Otosclerosis causes a build-up of bone around the stapes (stirrup bone). The build-up of bone keeps the stapes from moving normally, resulting in a type of hearing loss called conductive hearing loss. The surgery is done to replace the stapes with an artificial part. After the surgery, sound can again be transmitted from the eardrum to the inner ear. This surgery can restore normal hearing in more than 90% of cases.
This operation is used when the main cause of a hearing loss is decreased movement of the stapes (otosclerosis). If both ears have this problem, the ear with worse hearing is treated first.
Not everyone with otosclerosis needs this surgery. Sometimes the hearing loss is not bad enough to require surgery. Sometimes people choose a hearing aid to help their hearing instead of surgery. In some cases the surgery may be done to allow better use of a hearing aid.
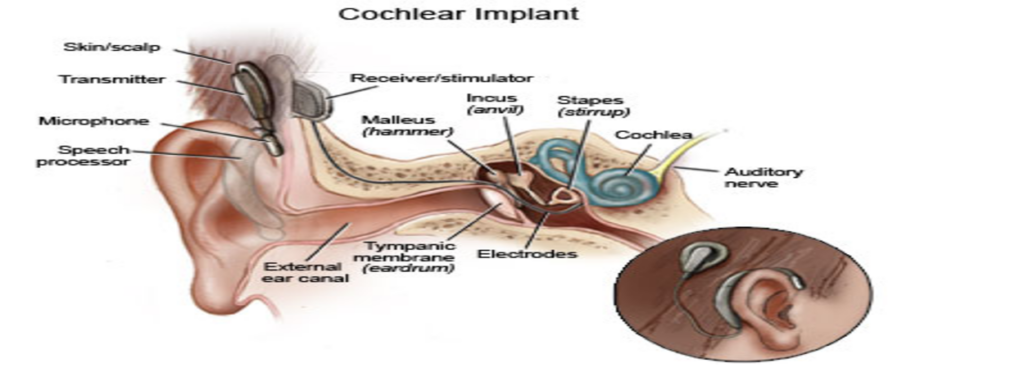
Cochlear Implantation
Head and Neck Cancer Surgery
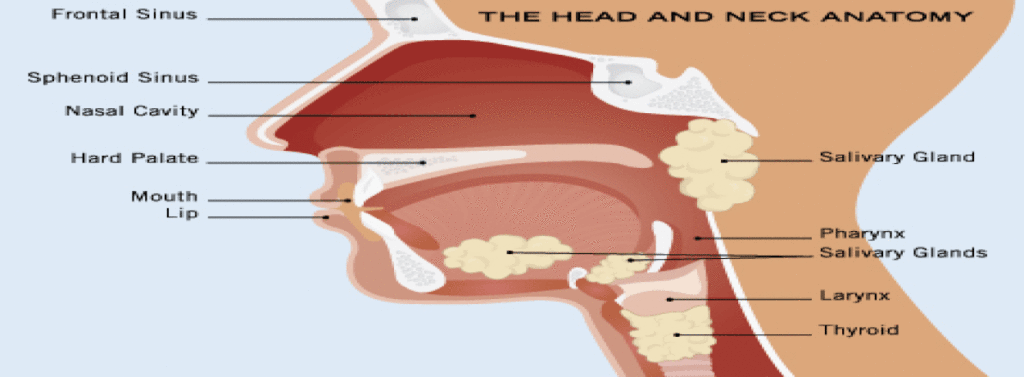
Cancers of the head and neck include malignancies of the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx (voice box), and neck. Historically such malignancies were often associated with tobacco and alcohol usage and those substances remain important etiologic factors. In recent years there has been a marked increase in the incidence of head and neck cancer (particularly malignancies of the tonsils and tongue base) caused by infection with the human papilloma virus (HPV).
Symptom of Head and Neck Cancer
1.Hoarseness
2.Difficulty swallowing
3.Painful swallowing
4.Throat pain
5.Weight loss
6.Persistent ear pain without hearing loss
7.Persistent neck mass (often painless)
8.Oral bleeding Stridor(noisy breathing)
Patients exhibiting any of these symptoms should be evaluated by one of the physicians at ENT and Allergy Associates as soon as possible.
Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer
There are numerous options to treat H&N cancer. The most common treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The optimal treatment must be individualized for each cancer and each patient, depending upon the type of cancer, the site of the cancer, the stage (extent) of the cancer, and the underlying health status of the patient.
These complex malignancies often require the expertise of numerous physicians and para health professionals (speech language pathologists, dieticians, physical therapists, occupational therapists) in different specialties working in a collaborative, team-oriented approach. Such specialists may include head and neck surgeons, plastic and reconstructive surgeons, skull base surgeons, neurosurgeons, radiation oncologists, and medical oncologists.
Head and Neck/ Endocrine procedure:
1.Thyroidectomy
2.Para thyroidectomy
3.Parotidectomy
4.Excision of submandibular gland for infection or tumor
5.Excision of benign and malignant laryngeal (voice box) tumors
6.Excision and reconstruction of tumors of the mouth, larynx, pharynx, and neck
7.Excisional of congenital masses of the head and neck
8.Excision and reconstruction of skin cancers of the head and neck
Some of these tumors involve more than one site in the head and neck, and it is not unusual for some tumors to require a team approach, including head and neck surgeons, plastic and reconstructive surgeons, rhinologists and skull base surgeons, and neurosurgeons.
• Parotidectomy
The parotid gland is the largest of the salivary glands, all of which produce saliva to help lubricate the oral cavity during meals. It is located just anterior to the ear, with extensions behind the ear and inferiorly into the upper neck. The most common indication for parotidectomy is tumors in the gland; the operation is rarely performed for severe, recurrent infections within the gland. Click here to read more… Fortunately, most parotid tumors (85-90%) are benign. The malignancies vary widely in their aggressiveness and prognosis; many low grade parotid cancers are highly curable with surgery. The most common parotid tumor is a pleomorphic adenoma, also called a benign mixed tumor. Pleomorphic adenomas have been known to degenerate into cancers if they are neglected for many years, hence the standard treatment for most parotid tumors is surgery.
• Hyperparathyroidism
The parathyroid glands are tiny glands in the neck that help to regulate the level of serum calcium. When the blood calcium level drops, the parathyroid glands release parathyroid hormone (PTH), which helps to raise the level of serum calcium. Once the serum calcium level returns to normal, PTH production usually stops. In hyperparathyroidism one or more parathyroid glands become independent and continue to produce PTH. As a result, the serum calcium climbs. The resulting hypercalcemia can result in metabolic complications such as kidney stones, osteoporosis, brittle bones that can easily fracture, and abdominal pain. Click here to read more…The most common symptom of hyperparathyroidism is probably fatigue, however, since there are so many other potential causes for fatigue, you can never be certain if it is parathyroid-related until after surgery. Some patients with hyperparathyroidism are completely asymptomatic.
Advanced Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) and Allergy
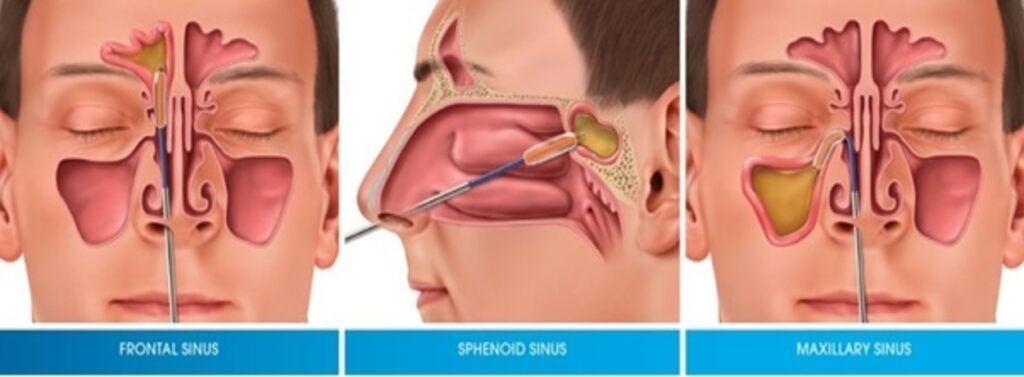
Chronic nasal and sinus conditions including chronic sinusitis, nasal polyps and chronic nasal obstruction which may result from a deviated nasal septum, enlarged nasal turbinate and nasal valve dysfunction all of which are essential for healthy breathing can be easily treated.
Chronic nasal obstruction is a common condition and may result from chronic allergies, nasal septal deviation, turbinate hypertrophy, dysfunction of the nasal valve, or sinus obstruction by nasal polyps, which can all hamper our ability to breathe properly.
Advanced technology is now available to enhance the accuracy and safety of complicated sinus and nasal surgery. We routinely perform and offer patients image guided sinus surgery and balloon sinuplasty, which have greatly enhanced patient safety, patient recovery and accuracy of nasal and sinus procedures. We also routinely perform septoplasty, turbinate reduction and nasal valve procedures to relieve nasal obstruction.
Septoplasty & Turbinate Hypertrophy
Nasal Septal Deviation and Turbinate hypertrophy can lead to nasal obstruction, resulting in an inability to breathe correctly. These conditions also impact chronic allergy symptoms and make it harder for traditional medical therapy to relieve allergy symptoms, most commonly nasal congestion. Septoplasty aims to improve nasal breathing by straightening out a deviated septum by removing the excess bone, tissue, and cartilage. In addition to septoplasty, it is often necessary to correct turbinate hypertrophy, which often results from chronic allergies, by also removing excess turbinate tissue. Widening the nasal valve may be needed as well in order to fully widen the nasal passages and enhance nasal breathing.
• Image Guided Technology
Image-guided technology revolutionizes traditional sinus surgical techniques by utilizing 3D Cat (CT) scan images to accurately navigate the nasal sinuses safely during surgery and correlate that patients anatomy in real time during surgery to the CT scan images. This enhances the accuracy and safety of endoscopic sinus procedures compared with traditional techniques.
• Image Guided Endoscopic Surgery & Nasal Polyps
Nasal polyps are a common cause of chronic sinusitis and nasal obstruction and are often accompanied with asthma or allergies. Nasal polyps often require sinus surgery to remove the polyps and open the nasal sinuses in order to relieved the nasal obstruction, improve breathing and improve sinus function. Image guided endoscopic sinus surgery allows surgery to be performed with greater accuracy and safety. With no external incisions, endoscopic surgery removes nasal polyps, clearing the passageways to allow proper drainage and air exchange.
• Balloon Sinuplasty
Balloon sinuplasty is an endoscopic, catheter-based technology utilized in treating chronic sinusitis and sinus obstruction. Balloon sinuplasty uses a small, flexible, sinus balloon catheter to open sinus passageways, restoring flow of mucous and sinus drainage. When inflated, balloon sinuplasty gently widens the natural openings of the nasal sinus passageways while maintaining the integrity of the sinus lining. Balloon sinuplasty is a relatively new, minimally invasive technique that has proven documented safety and improved patient recovery with minimal patient discomfort.
Surgery for Voice Disorders
Laser Surgery
Laser surgery is a common treatment for vocal cord cancer in its earliest stages. The laser enables microscopic precision that preserves as much normal tissue as possible, thus limiting the impact on the voice and swallowing after surgery. A one-time surgical operation can be offered as an alternative to six weeks of standard radiation therapy.
• Phonomicrosurgery
Phonomicrosurgery uses microsurgical instruments and techniques to improve vocal function. The technique is used in the following procedures to address problems with the voice, breathing, or swallowing.
1. Injection laryngoplasty, sometimes called vocal fold augmentation, which is the injection of a substance into one or both of the vocal cords to bring them closer together in order to produce a stronger voice.
2. Laryngoplasty is a procedure designed to permanently change the shape of the voice box to improve the voice.
3. Micro laryngoscopy, a surgical technique that uses a microscope and specialized micro instruments to perform extremely precise excisions and other interventions on the delicate structures of the vocal cords.
4. biopsy of throat lesions
5. laryngeal re innervation, which creates a new nerve supply for a paralyzed vocal cord.
6. tracheostomy, which is the insertion of a tube into the trachea, or windpipe, to enable easier breathing.
7. laryngectomy, the surgical removal of the voice box, which is most often used to treat advanced cancer of the larynx.
Tympanoplasty (eardrum repair)
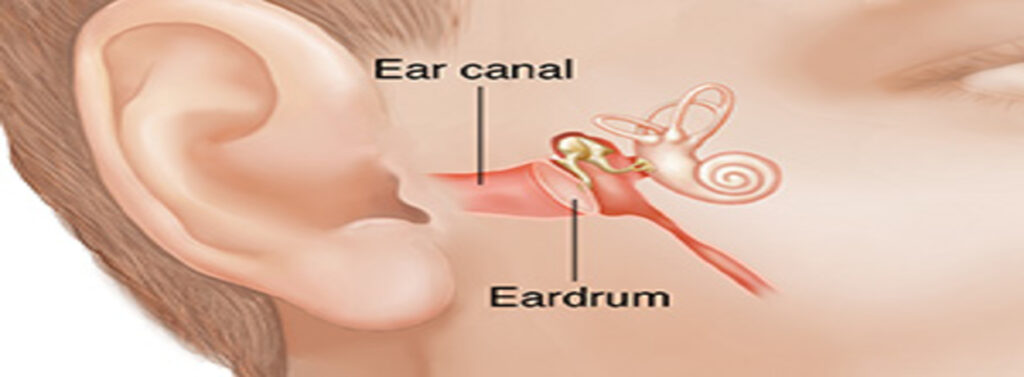
Tympanoplasty is the surgical procedure which restores and/or retains hearing. During the tympanoplasty, the surgeon will graft the tympanic membrane (eardrum) and reconstruct the middle ear. A prosthetic device may need to be implanted to replace the ossicles (middle ear bones) that have been damaged by infection.
Types of prosthetics used to replace the ossicles may be:
- T.O.R.P. (Total Ossicular Replacement Prosthesis)
- P.O.R.P. (Partial Ossicular Replacement Prosthesis)
The goal of tympanoplasty is to close any perforation, as well as improve hearing.
Rhinoplasty
Rhinoplasty is surgery to reshape the nose. It can make the nose larger or smaller; change the angle of the nose in relation to the upper lip; alter the tip of the nose; or correct bumps, indentations, or other defects in the nose.
During rhinoplasty, the surgeon makes incisions to access the bones and cartilage that support the nose. The incisions are usually made inside the nose so that they are invisible after the surgery. Depending on the desired result, some bone and cartilage may be removed, or tissue may be added (either from another part of the body or using a synthetic filler). After the surgeon has rearranged and reshaped the bone and cartilage, the skin and tissue is red raped over the structure of the nose. A splint is placed outside the nose to support the new shape of the nose as it heals.
Rhinoplasty may be done using general or local anaesthesia. It is usually done as an outpatient procedure but sometimes requires a 1-night stay in the hospital or surgery centre.
Surgeons who do rhinoplasties typically have training in either plastic surgery, otolaryngology (ear, nose, and throat specialty), or both.

Aarav Medicare team is ready to look after all your medical emergency needs. We will Take care of your health.
Saurav
Why Aarav Medicare?

Highly Qualified Specialists
Best Specialist Doctors for all the Treatment and Procedures. Get Free Online Consutations.
State Of The Art Facility
Finest Hospitals with all the modern Medical Equipment and Best Patient Care.

