Cancer/ Oncology – Types and Treatment
Cancer/ Oncology – Types and Treatment
About Cancer and types of treatment
Oncology is the study of cancer. An oncologist is a doctor who treats cancer. Usually, an oncologist manages a person’s care and treatment once he or she is diagnosed with cancer. The field of oncology has three major areas:
- Medical Oncology
- Surgical Oncology
- Radiation Oncology
A Medical Oncologist treats cancer using chemotherapy or other medications, such as targeted therapy.
A Surgical Oncologist removes the tumour and nearby tissue during an operation. He or she also performs certain types of biopsies.
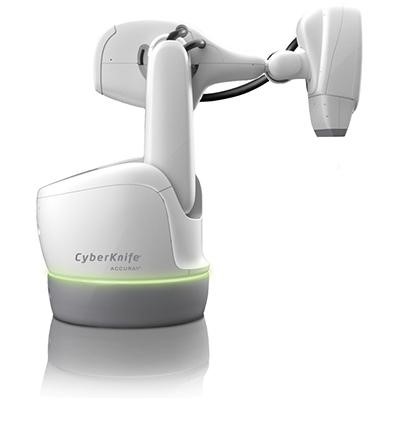
A Radiation Oncologist treats cancer using radiation therapy with:
- IGRT- Image-guided radiation therapy.
- IMRT-Intensity-modulated radiation therapy.
- Cyber Knife:- is a frameless robotic radiosurgery system used for treating benign tumors, malignant tumours and other medical conditions.
Other types of oncologists include the following:
A gynecologic oncologist treats gynaecologic cancers, such as uterine cancer and cervical cancer.
A pediatric oncologist treats cancer in children. Some types of cancer occur most often in children and teenagers, such as certain brain tumors, leukemia, osteosarcoma, and Ewing’s sarcoma. But they sometimes occur in adults. In these cases, an adult may decide to work with a pediatric oncologist.
A hematologist-oncologist diagnoses and treats blood cancers, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma.
There are many types of cancer treatment. The types of treatment that you receive will depend on the type of cancer you have and how advanced it is. Some people with cancer will have only one treatment. But most people have a combination of treatments, such as surgery with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy. When you need treatment for cancer, you have a lot to learn and think about. It is normal to feel overwhelmed and confused. But, talking with your doctor and learning about the types of treatment you may have can help you feel more in control.
Surgical Oncology

Radiation Therapy

Medical Oncology
Chemotherapy

Immunotherapy
Trageted Therapy
Hormone Therapy
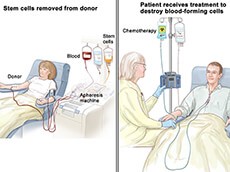
Stem Cell Therapy
Various Types of Cancer:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
- Adolescents, Cancer in
- Adrenocortical Carcinoma
- Childhood Adrenocortical Carcinoma – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Kaposi Sarcoma (Soft Tissue Sarcoma)
- AIDS-Related Lymphoma (Lymphoma)
- Primary CNS Lymphoma (Lymphoma)
- Anal Cancer
- Appendix Cancer – see Gastrointestinal Carcinoid Tumors
- Astrocytomas, Childhood (Brain Cancer)
- Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor, Childhood, Central Nervous System (Brain Cancer)
- Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Skin – see Skin Cancer
- Bile Duct Cancer
- Bladder Cancer
- Childhood Bladder Cancer – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Bone Cancer (includes Ewing Sarcoma and Osteosarcoma and Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma)
- Brain Tumors
- Breast Cancer
- Childhood Breast Cancer – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Bronchial Tumors, Childhood – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Burkitt Lymphoma – see Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Carcinoid Tumor (Gastrointestinal)
- Childhood Carcinoid Tumors – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Carcinoma of Unknown Primary
- Childhood Carcinoma of Unknown Primary – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Cardiac (Heart) Tumors, Childhood – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Central Nervous System
- Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor, Childhood (Brain Cancer)
- Embryonal Tumors, Childhood (Brain Cancer)
- Germ Cell Tumor, Childhood (Brain Cancer)
- Primary CNS Lymphoma
- Cervical Cancer
- Childhood Cervical Cancer – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Childhood Cancers
- Cancers of Childhood, Unusual
- Cholangiocarcinoma – see Bile Duct Cancer
- Chordoma, Childhood – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
- Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML)
- Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
- Colorectal Cancer
- Childhood Colorectal Cancer – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Craniopharyngioma, Childhood (Brain Cancer)
- Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma – see Lymphoma (Mycosis Fungoides and Sézary Syndrome)
- Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS) – see Breast Cancer
- Embryonal Tumors, Central Nervous System, Childhood (Brain Cancer)
- Endometrial Cancer (Uterine Cancer)
- Ependymoma, Childhood (Brain Cancer)
- Esophageal Cancer
- Childhood Esophageal Cancer – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Esthesioneuroblastoma (Head and Neck Cancer)
- Ewing Sarcoma (Bone Cancer)
- Extracranial Germ Cell Tumor, Childhood
- Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumor
- Eye Cancer
- Childhood Intraocular Melanoma – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Intraocular Melanoma
- Retinoblastoma
- Fallopian Tube Cancer
- Fibrous Histiocytoma of Bone, Malignant, and Osteosarcoma
- Gallbladder Cancer
- Gastric (Stomach) Cancer
- Childhood Gastric (Stomach) Cancer – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Gastrointestinal Carcinoid Tumor
- Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) (Soft Tissue Sarcoma)
- Childhood Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Germ Cell Tumors
- Childhood Central Nervous System Germ Cell Tumors (Brain Cancer)
- Childhood Extracranial Germ Cell Tumors
- Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors
- Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors
- Testicular Cancer
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
- Hairy Cell Leukemia
- Head and Neck Cancer
- Heart Tumors, Childhood – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Hepatocellular (Liver) Cancer
- Histiocytosis, Langerhans Cell
- Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Hypopharyngeal Cancer (Head and Neck Cancer)
- Intraocular Melanoma
- Childhood Intraocular Melanoma – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Islet Cell Tumors, Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
- Kaposi Sarcoma (Soft Tissue Sarcoma)
- Kidney (Renal Cell) Cancer
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
- Laryngeal Cancer (Head and Neck Cancer)
- Leukemia
- Lip and Oral Cavity Cancer (Head and Neck Cancer)
- Liver Cancer
- Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell and Small Cell)
- Childhood Lung Cancer – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Lymphoma
- Male Breast Cancer
- Malignant Fibrous
- Histiocytoma of Bone and Osteosarcoma
- Melanoma
- Childhood Melanoma – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
Melanoma, Intraocular (Eye) - Childhood Intraocular Melanoma – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Merkel Cell Carcinoma (Skin Cancer)
- Mesothelioma, Malignant
- Childhood Mesothelioma – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Metastatic Cancer
- Metastatic Squamous Neck Cancer with Occult Primary (Head and Neck Cancer)
- Midline Tract Carcinoma Involving NUT Gene
- Mouth Cancer (Head and Neck Cancer)
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndromes – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Multiple Myeloma/Plasma Cell Neoplasms
- Mycosis Fungoides (Lymphoma)
- Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
- Myelogenous Leukemia, Chronic (CML)
- Myeloid Leukemia, Acute (AML)
- Myeloproliferative Neoplasms, Chronic
- Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinus Cancer (Head and Neck Cancer)
- Nasopharyngeal Cancer (Head and Neck Cancer)
- Neuroblastoma
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Oral Cancer, Lip and Oral Cavity Cancer and Oropharyngeal Cancer (Head and Neck Cancer)
- Osteosarcoma and Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma of Bone
- Ovarian Cancer
- Childhood Ovarian Cancer – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
Pancreatic Cancer - Childhood Pancreatic Cancer – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (Islet Cell Tumors)
- Papillomatosis (Childhood Laryngeal)
- Paraganglioma
- Childhood Paraganglioma – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Paranasal Sinus and Nasal Cavity Cancer (Head and Neck Cancer)
- Parathyroid Cancer
- Penile Cancer
- Pharyngeal Cancer (Head and Neck Cancer)
- Pheochromocytoma
- Childhood Pheochromocytoma – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Pituitary Tumor
- Plasma Cell Neoplasm/Multiple Myeloma
- Pleuropulmonary Blastoma – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Pregnancy and Breast Cancer
- Primary Central Nervous System (CNS) Lymphoma
- Primary Peritoneal Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Rectal Cancer
- Recurrent Cancer
- Renal Cell (Kidney) Cancer
- Retinoblastoma
- Rhabdomyosarcoma, Childhood (Soft Tissue Sarcoma)
- Salivary Gland Cancer (Head and Neck Cancer)
- Sarcoma
- Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma (Soft Tissue Sarcoma)
- Childhood Vascular Tumors (Soft Tissue Sarcoma)
- Kaposi Sarcoma (Soft Tissue Sarcoma)
- Osteosarcoma (Bone Cancer)
- Uterine Sarcoma
- Sézary Syndrome (Lymphoma)
- Skin Cancer
- Childhood Skin Cancer – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Small Intestine Cancer
- Soft Tissue Sarcoma
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Skin – see Skin Cancer
- Squamous Neck Cancer with Occult Primary, Metastatic (Head and Neck Cancer)
- Stomach (Gastric) Cancer
- Childhood Stomach (Gastric) Cancer – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- T-Cell Lymphoma, Cutaneous – see Lymphoma (Mycosis Fungoides and Sèzary Syndrome)
- Testicular Cancer
- Childhood Testicular Cancer – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Throat Cancer (Head and Neck Cancer)
- Nasopharyngeal Cancer
- Oropharyngeal Cancer
- Hypopharyngeal Cancer
- Thymoma and Thymic Carcinoma
- Thyroid Cancer
- Transitional Cell Cancer of the Renal Pelvis and Ureter (Kidney (Renal Cell) Cancer)
- Unknown Primary, Carcinoma of
- Childhood Cancer of Unknown Primary – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Ureter and Renal Pelvis, Transitional Cell Cancer (Kidney (Renal Cell) Cancer
- Urethral Cancer
- Uterine Cancer, Endometrial
- Uterine Sarcoma
- Vaginal Cancer
- Childhood Vaginal Cancer – see Unusual Cancers of Childhood
- Vascular Tumors (Soft Tissue Sarcoma)
- Vulvar Cancer

Aarav Medicare team is ready to look after all your medical emergency needs. We will Take care of your health.
Saurav
Why Aarav Medicare?

Highly Qualified Specialists
Best Specialist Doctors for all the Treatment and Procedures. Get Free Online Consutations.
State Of The Art Facility
Finest Hospitals with all the modern Medical Equipment and Best Patient Care.
